In the past year, creatives have earned billions of dollars selling digital art, collectibles, and game items to their true fans using NFTs. NFTs are tokens that represent ownership of unique assets on a blockchain. Each NFT project has a smart contract that lives on the blockchain and keeps track of who owns which asset.
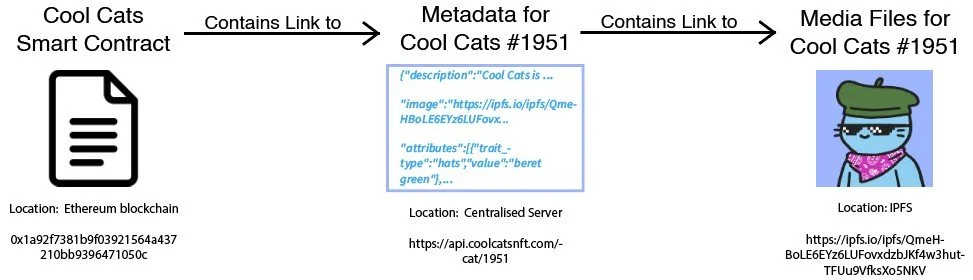
The core of every NFT is its metadata. This metadata consists of a description of the NFT (name, attributes, properties, etc.) and a pointer to its media files (images, video, audio, etc.).
Storing this information directly on a blockchain is expensive, so most NFT projects store their data elsewhere and only keep a link to it in their smart contract.
Example of a common NFT data structure
In this piece, I will:
Outline the strengths and weaknesses of different NFT data storage methods
investigate each method’s level of adoption
Discuss the future of NFT data storage